Your cart is currently empty!
Nvember 12, 2021
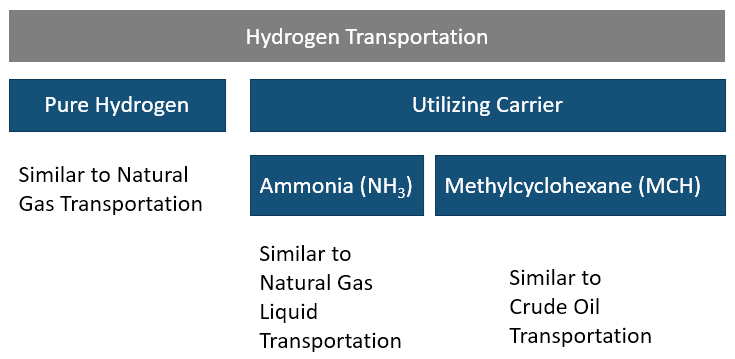
Hydrogen has high energy per weight, however, has low density therefore; low energy per volume. Having low boiling point (-253 degrees C) and low-density results in challenges in storage and transportation. Can be shipped as pure Hydrogen or utilizing a Hydrogen carrier, via ammonia (NH3) and Methylcyclohexane (MCH).
Pipeline Blending
- Hydrogen blending into natural gas pipelines is considered an option to grow hydrogen capability without the large upfront costs and time of developing a dedicated hydrogen pipeline network.
- Hydrogen as a renewable gas, with associated credits, could be important in utilising the North American natural gas pipeline grid.
- SMR in combination with CCS could utilise the North American pipeline grid to provide low/no carbon option.
- Economic incentive for converting excess curtailed energy from renewable sources (wind, solar) into hydrogen.
- Safety is the most important factor for operators of natural gas pipelines throughout North America.
- 2013 NREL study* concluded low concentrations (<5-15% hydrogen by volume) of hydrogen blending in Natural gas pipelines was viable.
- Enbridge Gas received permission from the Ontario Energy Board to blend up to 2% hydrogen** from Electrolysis in Markham, Ontario.
- Hydrogen is lower density than natural gas therefore, requires 30% more pipeline space to delivery the same energy (Btu basis).
* Blending Hydrogen into Natural Gas Pipeline Networks: A Review of Key Issues
** OEB Decision EB-2019-0294
See also:
Hydrogen Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) 2021
Carbon Capture and Storage for Hydrogen 2021
Low Carbon Ammonia Plant 2021
Hydrogen Pipeline 2021
Methylcyclohexane (MHC)-Toluene Hydrogenation 2021

